High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a widespread health concern affecting millions globally. Managing blood pressure effectively is crucial for preventing serious conditions like heart disease and stroke. While lifestyle changes such as diet and medication are common solutions, scientific research has shown that isometric exercises can significantly contribute to lowering blood pressure naturally. This article explores the benefits, mechanisms, and best practices of isometric exercises for managing hypertension.
What Are Isometric Exercises?
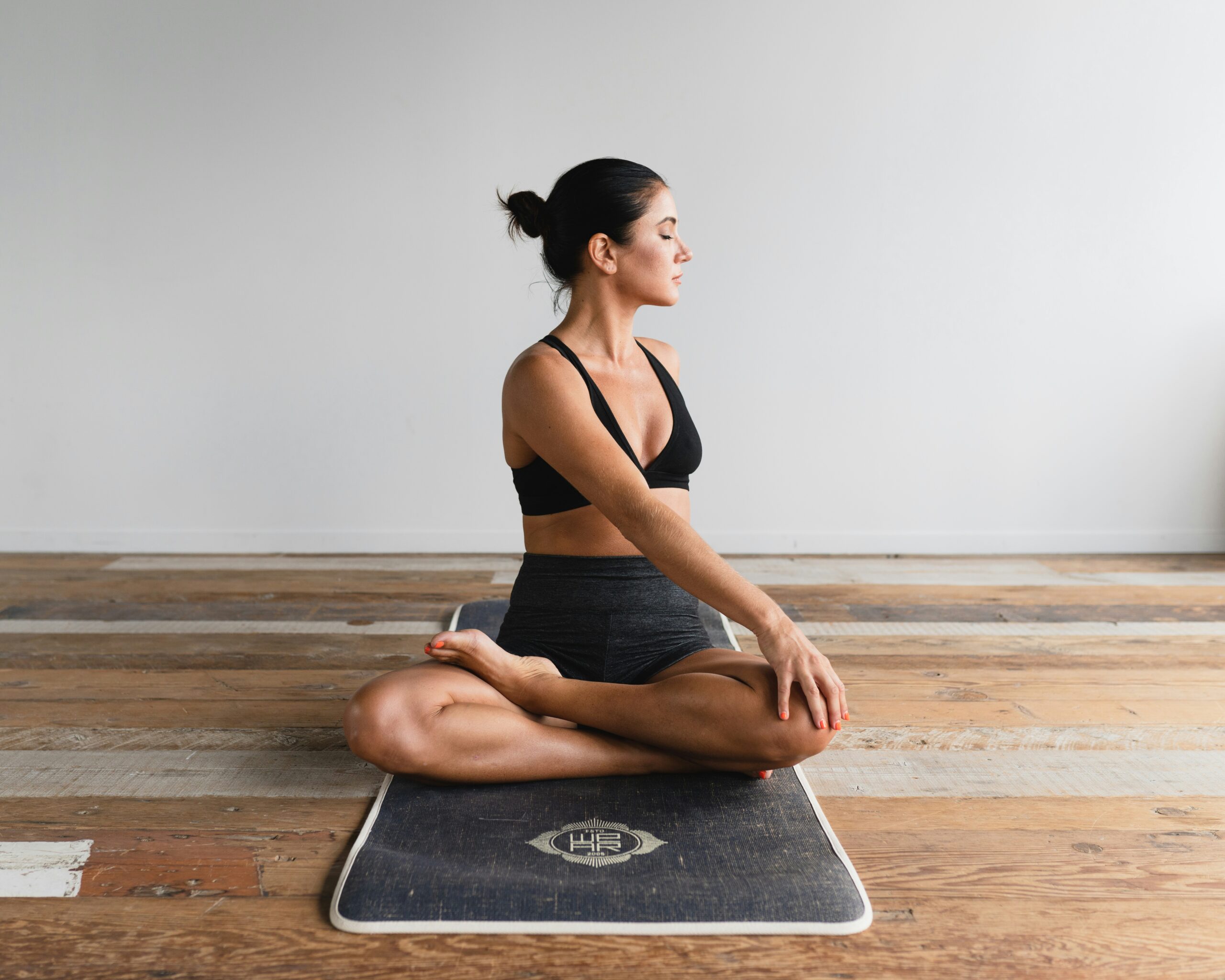
Isometric exercises are a type of strength training where muscles contract without changing length and without any visible joint movement. Unlike dynamic exercises such as running or lifting weights, isometric exercises involve maintaining a fixed position under tension for a set period.
Examples of Isometric Exercises:
- Plank: Holding a plank position for 30 to 60 seconds.
- Wall Sit: Leaning against a wall in an invisible chair position.
- Handgrip Exercise: Squeezing a handgrip device or a soft ball for a specified duration.
- Static Squat Hold: Holding a squat position without movement.
- Isometric Push-Up Hold: Holding the push-up position at mid-point without lowering or rising.
How Do Isometric Exercises Help Control Blood Pressure?
Several scientific studies have indicated that isometric exercises positively influence blood pressure regulation through various physiological mechanisms. Here’s how they help:
1. Enhanced Vascular Function
Holding an isometric position increases intramuscular pressure, temporarily restricting blood flow. When released, the blood rushes back through the vessels, leading to improved endothelial function and flexibility of arteries. This process enhances circulation and contributes to lower blood pressure over time.
2. Reduction of Peripheral Resistance
Hypertension often results from increased resistance in blood vessels. Isometric exercises help to reduce vascular resistance, allowing blood to flow more easily, thus lowering overall blood pressure.
3. Activation of the Parasympathetic Nervous System
These exercises stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for relaxation and recovery. This activation helps to decrease stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which are known to contribute to high blood pressure.
4. Improved Baroreceptor Sensitivity
Baroreceptors are sensors in the arteries that help regulate blood pressure. Regular isometric training improves their sensitivity, helping the body maintain stable blood pressure levels more efficiently.
5. Stress Reduction and Mental Relaxation
Stress is a significant contributor to high blood pressure. Isometric exercises promote mental relaxation by stimulating the release of endorphins, which help reduce stress and anxiety levels.
How Often Should You Do Isometric Exercises?
To gain optimal benefits for blood pressure control, experts recommend performing isometric exercises 3 to 4 times per week. Each session should include multiple sets lasting 2 to 4 minutes per exercise, with short rest intervals in between.
Sample Isometric Exercise Routine for Blood Pressure Control:
- Wall Sit – Hold for 2 minutes, repeat 3 times.
- Plank – Hold for 1 minute, repeat 3 times.
- Handgrip Squeeze – Hold for 30 seconds per hand, repeat 4 times.
- Static Squat Hold – Hold for 1 minute, repeat 3 times.
Precautions and Considerations
While isometric exercises are generally safe, individuals with severe hypertension or cardiovascular conditions should consult a healthcare professional before beginning any new exercise regimen. It is essential to:
- Breathe steadily during exercises to avoid excessive spikes in blood pressure.
- Avoid excessive straining or holding breath (Valsalva maneuver), which can temporarily increase blood pressure.
- Gradually increase the duration and intensity of exercises over time.
Conclusion
Isometric exercises provide an effective, simple, and convenient method for managing high blood pressure. They improve vascular function, reduce resistance in blood vessels, and help regulate stress hormones. Incorporating these exercises into your routine, along with a healthy lifestyle, can be a powerful strategy for maintaining optimal blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health. Start today and take a step toward better heart health with isometric exercises!